The Hidden Truth about the War in Ukraine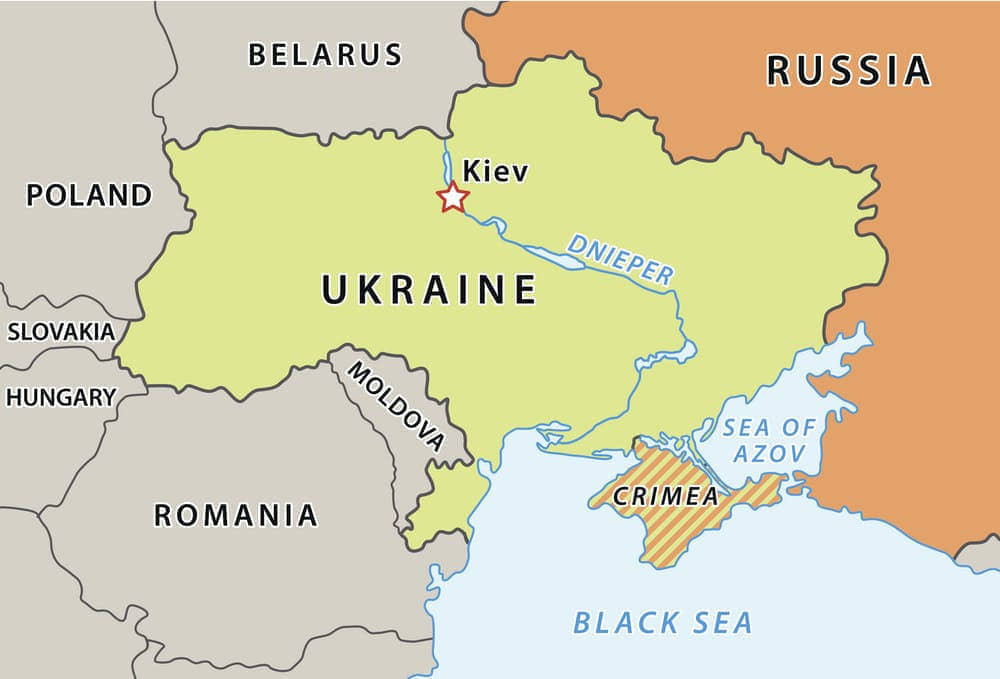
The cultural and historical elements that determine the relations between Russia and Ukraine are important. The two countries have a long, rich, diverse, and eventful history together.
This would be essential if the crisis we are experiencing today were rooted in history. However, it is a product of the present. The war we see today does not come from our great-grandparents, our grandparents or even our parents. It comes from us. We created this crisis. We created every piece and every mechanism. We have only exploited existing dynamics and exploited Ukraine to satisfy an old dream: to try to bring down Russia. Chrystia Freeland’s, Antony Blinken’s, Victoria Nuland’s and Olaf Scholz’s grandfathers had that dream; we realized it.
The way we understand crises determines the way we solve them. Cheating with the facts leads to disaster. This is what is happening in Ukraine. In this case the number of issues is so enormous that we will not be able to discuss them here. Let me just focus on some of them.
Did James Baker make Promises to Limit Eastward Expansion of NATO to Mikhail Gorbachev in 1990?
In 2021, NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg stated that “there was never a promise that NATO would not expand eastward after the fall of the Berlin Wall.” This claim remains widespread among self-proclaimed experts on Russia, who explain that there were no promises because there was no treaty or written agreement. This argument is a bit simplistic and false.
It is true that there are no treaties or decisions of the North Atlantic Council (NAC) that embody such promises. But this does not mean that they have not been formulated, nor that they were formulated out of casualness!
Today we have the feeling that having “lost the Cold War,” the USSR had no say in the European security developments. This is not true. As a winner of the Second World War, the USSR had a de jure a veto right over German reunification. In other words, Western countries had to obtain its agreement, in exchange for which Gorbachev demanded a commitment to the non-expansion of NATO. It should not be forgotten that in 1990 the USSR still existed, and there was no yet question to dismantle it, as the referendum of March 1991 would show. The Soviet Union was therefore not in a weak position and could prevent the reunification.
This was confirmed by Hans-Dietrich Genscher, the German Foreign Minister, in Tutzing (Bavaria) on 31 January 1990, as reported in a cable from the U.S. embassy in Bonn:
Genscher warned, however, that any attempt to expand [NATO’s] military reach into the territory of the German Democratic Republic (GDR) would block German reunification.
German reunification had two major consequences for the USSR: the withdrawal of the Group of Soviet Forces in Germany (GSFG), the most powerful and modern contingent outside its territory, and the disappearance of a significant part of its protective “glacis.” In other words, any move would be at the expense of its security. This is why Genscher stated:
…The changes in Eastern Europe and the process of German unification should not “undermine Soviet security interests.” Therefore, NATO should exclude an “expansion of its territory to the East, i.e. to get closer to the Soviet borders.”
At this stage, the Warsaw Pact was still in force and the NATO doctrine was unchanged. Therefore Mikhail Gorbachev expressed very soon his legitimate concerns for USSR national security. This is what prompted James Baker, the American Secretary of State, to immediately begin discussions with him. On 9 February 1990, in order to appease Gorbachev’s concerns, Baker declared:
Not only for the Soviet Union but also for other European countries, it is important to have guarantees that if the United States maintains its presence in Germany within the framework of NATO, not one inch of NATO’s current military jurisdiction will spread eastward.
Promises were thus made simply because the West had no alternative, to obtain the USSR’s approval; and without promises Germany would not have been reunified. Gorbachev accepted German reunification only because he had received assurances from President George H.W. Bush and James Baker, Chancellor Helmut Kohl and his Foreign Minister Hans-Dietrich Genscher, British Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher, her successor John Major and their Foreign Minister Douglas Hurd, President François Mitterrand, but also from CIA Director Robert Gates and Manfred Wörner, then Secretary General of NATO.
Thus, on 17 May 1990, in a speech in Brussels, Manfred Wörner, NATO Secretary-Geenral, declared:
The fact that we are prepared not to deploy a NATO army beyond German territory gives the Soviet Union a solid guarantee of security.
In February 2022, in the German magazine Der Spiegel, Joshua Shifrinson, an American political analyst, revealed a declassified SECRET document of March 6, 1991, written after a meeting of the political directors of the foreign ministries of the United States, Great Britain, France and Germany. It reports the words of the German representative, Jürgen Chrobog:
We made it clear in the 2+4 negotiations that we would not extend NATO beyond the Elbe. Therefore, we cannot offer NATO membership to Poland and the others.
The representatives of the other countries also accepted the idea of not offering NATO membership to the other Eastern European countries.
So, written record or not, there was a “deal,” simply because a “deal” was inevitable. Now, in international law, a “promise” is a valid unilateral act that must be respected (“promissio est servanda“). Those who deny this today are simply individuals who do not know the value of a given word.
Did Vladimir Putin disregard the Budapest Memorandum (1994)
In February 2022, at the Munich Security Forum, Volodymyr Zelensky referred to the 1994 Budapest Memorandum and threatened to become a nuclear power again. However, it is unlikely that Ukraine will become a nuclear power again, nor will the nuclear powers allow it to do so. Zelensky and Putin know this. In Fact, Zelensky is not using this memorandum to get nuclear weapons, but to get Crimea back, since the Ukrainians see Russia’s annexation of Crimea as a violation of this treaty. Basically, Zelensky is trying to hold Western countries hostage. To understand that we must go back to events and facts that are opportunistically “forgotten” by our historians.
On 20 January 1991, before the independence of Ukraine, the Crimeans were invited to choose by referendum between two options: to remain with Kiev or to return to the pre-1954 situation and be administered by Moscow. The question asked on the ballot was:
Are you in favor of the restoration of the Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic of Crimea as a subject of the Soviet Union and a member of the Union Treaty?
This was the first referendum on autonomy in the USSR, and 93.6% of Crimeans agreed to be attached to Moscow. The Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic of Crimea (ASSR Crimea), abolished in 1945, was thus re-established on 12 February 1991 by the Supreme Soviet of the Ukrainian SSR. On 17 March, Moscow organized a referendum for the maintenance of the Soviet Union, which would be accepted by Ukraine, thus indirectly validating the decision of the Crimeans. At this stage, Crimea was under the control of Moscow and not Kiev, while Ukraine was not yet independent. As Ukraine organized its own referendum for independence, the participation of the Crimeans remained weak, because they did not feel concerned anymore.
Ukraine became independent six months after Crimea, and after the latter had proclaimed its sovereignty on September 4. On February 26, 1992, the Crimean parliament proclaimed the “Republic of Crimea” with the agreement of the Ukrainian government, which granted it the status of a self-governing republic. On 5 May 1992, Crimea declared its independence and adopted a Constitution. The city of Sevastopol, managed directly by Moscow in the communist system, had a similar situation, having been integrated by Ukraine in 1991, outside of all legality. The following years were marked by a tug of war between Simferopol and Kiev, which wanted to keep Crimea under its control.
In 1994, by signing the Budapest Memorandum, Ukraine surrendered the nuclear weapons of the former USSR that remained on its territory, in exchange for “its security, independence and territorial integrity.” At this stage, Crimea considered that it was—de jure—no longer part of Ukraine and therefore not concerned by this treaty. On its side, the government in Kiev felt strengthened by the memorandum. This is why, on 17 March 1995, it forcibly abolished the Crimean Constitution. It sent its special forces to overthrow Yuri Mechkov, President of Crimea, and de facto annexed the Republic of Crimea, thus triggering popular demonstrations for the attachment of Crimea to Russia. An event hardly reported by the Western media.
Crimea was then governed in an authoritarian manner by presidential decrees from Kiev. This situation led the Crimean Parliament to formulate a new constitution in October 1995, which re-established the Autonomous Republic of Crimea. This new constitution was ratified by the Crimean Parliament on 21 October 1998 and confirmed by the Ukrainian Parliament on 23 December 1998. These events and the concerns of the Russian-speaking minority led to a Treaty of Friendship between Ukraine and Russia on 31 May 1997. In the treaty, Ukraine included the principle of the inviolability of borders, in exchange—and this is very important—for a guarantee of “the protection of the ethnic, cultural, linguistic and religious originality of the national minorities on their territory.”
On 23 February 2014, not only did the new authorities in Kiev emerge from a coup d’état that had definitely no constitutional basis and were not elected; but, by abrogating the 2012 Kivalov-Kolesnichenko law on official languages, they no longer respected this guarantee of the 1997 treaty. The Crimeans therefore took to the streets to demand the “return” to Russia that they had obtained 30 years earlier.
On March 4, during his press conference on the situation in Ukraine a journalist asked Vladimir Putin, “How do you see the future of Crimea? Do you consider the possibility that it joins Russia?” he replied:
No, we do not consider it. In general, I believe that only the residents of a given country who are free to decide and safe can and should determine their future. If this right has been granted to the Albanians in Kosovo, if this has been made possible in many parts of the world, then no one is excluding the right of nations to self-determination, which, as far as I know, is laid down in several UN documents. However, we will in no way provoke such a decision and will not feed such feelings.
On March 6, the Crimean Parliament decided to hold a popular referendum to choose between remaining in Ukraine or requesting the attachment to Moscow. It was after this vote that the Crimean authorities asked Moscow for an attachment to Russia.
With this referendum, Crimea had only recovered the status it had legally acquired just before the independence of Ukraine. This explains why it renewed its request to be attached to Moscow, as in January 1991.
Moreover, the status of force agreement (SOFA) between Ukraine and Russia for the stationing of troops in Crimea and Sevastopol had been renewed in 2010 and to run until 2042. Russia therefore had no specific reason to claim this territory. The population of Crimea, which legitimately felt betrayed by the government of Kiev, seized the opportunity to assert its rights.
On 19 February 2022, Anka Feldhusen, the German ambassador in Kiev, threw a spanner in the works by declaring on the television channel Ukraine 24 that the Budapest Memorandum was not legally binding. Incidentally, this is also the American position, as shown by the statement on the website of the American embassy in Minsk.
The whole Western narrative about the “annexation” of Crimea is based on a rewriting of history and the obscuring of the 1991 referendum, which did exist and was perfectly valid. The 1994 Budapest Memorandum remains extensively quoted since February 2022, but the Western narrative simply ignores the 1997 Friendship Treaty which is the reason for the discontent of the Russian-speaking Ukrainian citizens.
Is the Ukrainian Government Legitimate?
The Russians still see the regime change that occurred in 2014 as illegitimate, as it was not done through constitutional process and without any support from a large part of the Ukrainian population.
The Maidan revolution can be broken down into several sequences, with different actors. Today, those who are driven by hatred of Russia are trying to merge these different sequences into one single “democratic impulse”: A way to validate the crimes committed by Ukraine and its neo-Nazis zealots.
At first, the population of Kiev, disappointed by the government’s decision to postpone the signing of the treaty with the EU, gathered in the streets. Regime change was not in the air. This was a simple expression of discontent.
Contrary to what the West claims, Ukraine was then deeply divided on the issue of rapprochement with Europe. A survey conducted in November 2013 by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology (KIIS) shows that it was split almost exactly “50/50” between those who favored an agreement with the European Union and those favoring a customs union with Russia. In the south and east of Ukraine, industry was strongly linked to Russia, and workers feared that an agreement excluding Russia would kill their jobs. That is what would eventually happen. In fact, at this stage, the aim was already to try to isolate Russia.
In the Washington Post, Henry Kissinger, Ronald Reagan’s National Security Advisor, noted that the European Union “helped turn a negotiation into a crisis.”
What happened later involved ultranationalist and neo-Nazis groups coming from the Western part of the country. Violence erupted and the government withdrew, after signing an agreement with the rioters for new elections. But this was quickly forgotten.
It was nothing less than a coup d’état, led by the United States with the support of the European Union, and carried out without any legal basis, against a government whose election had been qualified by the OSCE as “transparent and honest” and having “offered an impressive demonstration of democracy.” In December 2014, George Friedman, president of the American geopolitical intelligence platform STRATFOR, said in an interview:
Russia defines the event that took place at the beginning of this year [in February 2014] as a coup organized by the US. And as a matter of fact, it was the most blatant [coup] in history.
Unlike European observers, the Atlantic Council, despite being strongly in favor of NATO, was quick to note that the Maidan revolution had been hijacked by certain oligarchs and ultra-nationalists. It noted that the reforms promised by Ukraine had not been carried out and that the Western media stuck to an acritical “black and white” narrative.
A telephone conversation between Victoria Nuland, then Assistant Secretary of State for Europe and Eurasia, and Geoffrey Pyatt, the U.S. ambassador to Kiev, revealed by the BBC, shows that the Americans themselves selected the members of the future Ukrainian government, in defiance of the Ukrainians and the Europeans. This conversation, which became famous thanks to Nuland’s famous “F*** the EU!”
The coup d’état was not unanimously supported by the Ukrainian people, either in substance or in form. It was the work of a minority of ultra-nationalists from western Ukraine (Galicia), who did not represent the whole Ukrainian people. Their first legislative act, on 23 February 2014, was to abrogate the 2012 Kivalov-Kolesnichenko law, which established the Russian language as an official language along with Ukrainian. This is what prompted the Russian-speaking population to start massive protests in the southern part of the country, against authorities they had not elected.
In July 2019, the International Crisis Group (funded by several European countries and the Open Society Foundation), noted:
The conflict in eastern Ukraine began as a popular movement. […]
The protests were organized by local citizens claiming to represent the Russian-speaking majority in the region. They were concerned both about the political and economic consequences of the new government in Kiev and about that government’s later abandoned measures to prevent the official use of the Russian language throughout the country [“Rebels without a Cause: Russia’s Proxies in Eastern Ukraine,” International Crisis Group, Europe Report N° 254, 16 juillet 2019, p. 2].
Western efforts to legitimate this far-right coup in Kiev led to hide the opposition in the southern part of the country. In order to present this revolution as democratic, the real “hand of the West” was cleverly masked by the imaginary “hand of Russia.” This is how the myth of a Russian military intervention was created. Allegations about a Russian military presence were definitely false, an event the chief of the Ukrainian Security service (SBU) confessed in 2015 that there were no Russian units in Donbass.
To make things worse, Ukraine didn’t gain legitimacy through the way it handled the rebellion. In 2014-2015, poorly advised by NATO military, Ukraine waged a war that could only lead to its defeat: it considered the populations of Donbass and Crimea as enemy foreign forces and made no attempt to win the “hearts and minds” of the autonomists. Instead, its strategy has been to punish the people even further. Bank services were stopped, economic relations with the autonomous regions were simply cut, and Crimea didn’t receive drinking water anymore.
This is why there are so many civilian victims in the Donbass, and why the Russian population still stands in majority behind its government today. The 14,000 victims of the conflict tend to be attributed to the “Russian invaders” and the so-called “separatists.” However, according to the United Nations—more than 80% of civilian casualties are the result of Ukrainian shelling. As we can see, the Ukrainian government is massacring its own people with the help, funding and advice of the military of NATO, the countries of the European Union, which defends its values.
In May 2014, the violent repression of protests prompted the population of some areas of the Donetsk and Lugansk regions of Ukraine to hold referendums for Self-Determination in the Donetsk People’s Republic (approved by 89%) and in the Lugansk People’s Republic (approved by 96%). Although Western media keeps calling them referendums of “independence,” they are referendums of “self-determination” or “autonomy” (самостоятельность). Until February 2022, our media consistently talked about “separatists” and “separatist republics.” In reality, as stated in the Minsk Agreement, these self-proclaimed republics didn’t seek “independence,” but an “autonomy” within Ukraine, with the ability to use their own language and their own customs.
Is NATO a Defensive Alliance?
NATO’s rationale is to bring European Allies under the US nuclear umbrella. It was designed as a defensive alliance, although recently declassified US documents show that the Soviets had apparently no intention to attack the West.
For the Russians, the question about whether NATO is offensive or defensive is beside the point. To understand Putin’s point of view, we have to consider two things that are usually overlooked by Western commentators: the enlargement of NATO towards the East, and the incremental abandonment of the international security’s normative framework by the US.
In fact, as long as the US didn’t deploy missiles in the vicinity of its borders, Russia didn’t bother so much about NATO extension. Russia itself considered to apply for membership. But problems stated to appear in 2001, as George W. Bush decided to unilaterally withdraw from the ABM Treaty and to deploy anti-ballistic missiles (ABM) in Eastern Europe. The ABM Treaty was intended to limit the use of defensive missiles, with the rationale of maintaining the deterrent effect of a mutual destruction by allowing the protection of decision-making bodies by a ballistic shield (in order to preserve a negotiating capacity). Thus, it limited the deployment of anti-ballistic missiles to certain specific zones (notably around Washington DC and Moscow) and prohibited it outside national territories.
Since then, the United States has progressively withdrawn from all the arms control agreements established during the Cold War: the ABM Treaty (2002), the Open Skies Treaty (2018) and the Intermediate-range Nuclear Forces (INF) Treaty (2019).
In 2019, Donald Trump justified his withdrawal from the INF Treaty by alleged violations by the Russian side. But, as the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) notes, the Americans never provided proof of these violations. In fact, the US was simply trying to get out of the agreement in order to install their AEGIS missile systems in Poland and Romania. According to the US administration, these systems are officially intended to intercept Iranian ballistic missiles. But there are two problems that clearly cast doubt on the good faith of the Americans:
- The first one is that there is no indication that the Iranians are developing such missiles, as Michael Ellemann of Lockheed-Martin stated before a committee of the American Senate.
- The second one is that these systems use Mk41 launchers, which can be used to launch either anti-ballistic missiles or nuclear missiles. The Radzikowo site, in Poland, is 800 km from the Russian border and 1,300 km from Moscow.
The Bush and Trump administrations said that the systems deployed in Europe were purely defensive. However, even if theoretically true, it is technically and strategically false. For the doubt, which allowed them to be installed, is the same doubt that the Russians could legitimately have in the event of a conflict. This presence in the immediate vicinity of Russia’s national territory can indeed lead to a nuclear conflict. For in the event of a conflict, it would not be possible to know precisely the nature of the missiles loaded in the systems—should the Russians therefore wait for explosions before reacting? In fact, we know the answer: having no early-warning time, the Russians would have practically no time to determine the nature of a fired missile and would thus be forced to respond pre-emptively with a nuclear strike.
Not only does Vladimir Putin see this as a risk to Russia’s security, but he also notes that the United States is increasingly disregarding international law in order to pursue a unilateral policy. This is why Vladimir Putin says that European countries could be dragged into a nuclear conflict without wanting to. This was the substance of his speech in Munich in 2007, and he came with the same argument early 2022, as Emmanuel Macron went to Moscow in February.
Finland and Sweden in NATO—A Good Idea?
The future will tell if Sweden’s and Finland’s decision to apply for NATO membership was a wise idea. They probably overstated the value of the nuclear protection offered by NATO. As a matter of fact, it is very unlikely that the US will sacrifice its national soil by striking Russian soil for the sake of Sweden or Finland. It is more likely that if the US engages nuclear weapons, it will be primarily on European soil and only as a last resort on Russian territory, in order to preserve its own territory from nuclear counter-strike.
Further, these two countries, which met the criteria of neutrality that Russia would want for its direct neighbors, deliberately put themselves in Russia’s nuclear crosshairs. For Russia, the main threat comes from the Central European theater of war. In other words, in the event of a hypothetical conflict in Europe, Russian forces would be engaged primarily in Central Europe, and could use their theater nuclear armies to “flank” their operations by striking the Nordic countries, with virtually no risk of a U.S. nuclear response.
Was it Impossible to Leave the Warsaw Pact?
The Warsaw Pact was created just after Germany joined NATO, for exactly the same reasons we have described above. Its largest military engagement was the invasion of Czechoslovakia in August 1968 (with the participation of all Pact nations, except Albania and Romania). This event resulted in Albania withdrawing from the Pact less than a month later, and Romania ceasing to participate actively in the military command of the Warsaw Pact after 1969. Therefore, asserting that no one was free to leave the treaty is not correct.
Jacques Baud is a widely respected geopolitical expert whose publications include many articles and books, including Poutine: Maître du jeu? Gouverner avec les fake news, and L’Affaire Navalny.



Geen opmerkingen:
Een reactie posten